Page 27 - Demo
P. 27
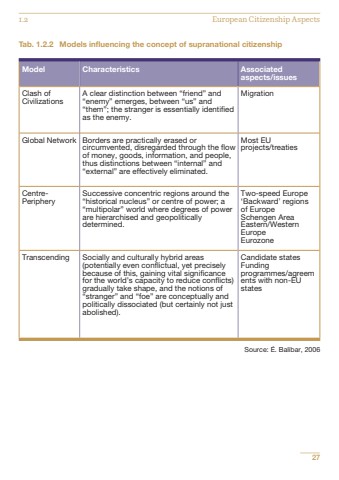
Tab. 1.2.2 Models influencing the concept of supranational citizenshipSource: %u00c9. Balibar, 2006271.2 European Citizenship AspectsModel Characteristics Associatedaspects/issuesClash ofCivilizationsA clear distinction between %u201cfriend%u201d and%u201cenemy%u201d emerges, between %u201cus%u201d and%u201cthem%u201d; the stranger is essentially identifiedas the enemy.MigrationGlobal Network Borders are practically erased orcircumvented, disregarded through the flowof money, goods, information, and people,thus distinctions between %u201cinternal%u201d and%u201cexternal%u201d are effectively eliminated.Most EUprojects/treatiesCentrePeripherySuccessive concentric regions around the%u201chistorical nucleus%u201d or centre of power; a%u201cmultipolar%u201d world where degrees of powerare hierarchised and geopoliticallydetermined.Two-speed Europe%u2018Backward%u2019 regions of EuropeSchengen AreaEastern/WesternEuropeEurozoneTranscending Socially and culturally hybrid areas(potentially even conflictual, yet preciselybecause of this, gaining vital significancefor the world%u2019s capacity to reduce conflicts)gradually take shape, and the notions of%u201cstranger%u201d and %u201cfoe%u201d are conceptually andpolitically dissociated (but certainly not justabolished).Candidate statesFundingprogrammes/agreements with non-EUstates